之前写了并查集的按秩优化,也就是按照size或者按照rank优化。
我们看下find函数,每次都要一步一步向上查找,直到根节点,如果find函数使用次数非常多的时候,每次都要查找好多次,时间复杂度为O(logn),但是如果我们直接把所有子结点全部指向根节点的话,也就是说这个时候,树已经变成了两层,查询起来,只需要查询一次就能查找到根节点。就向下图中的那样
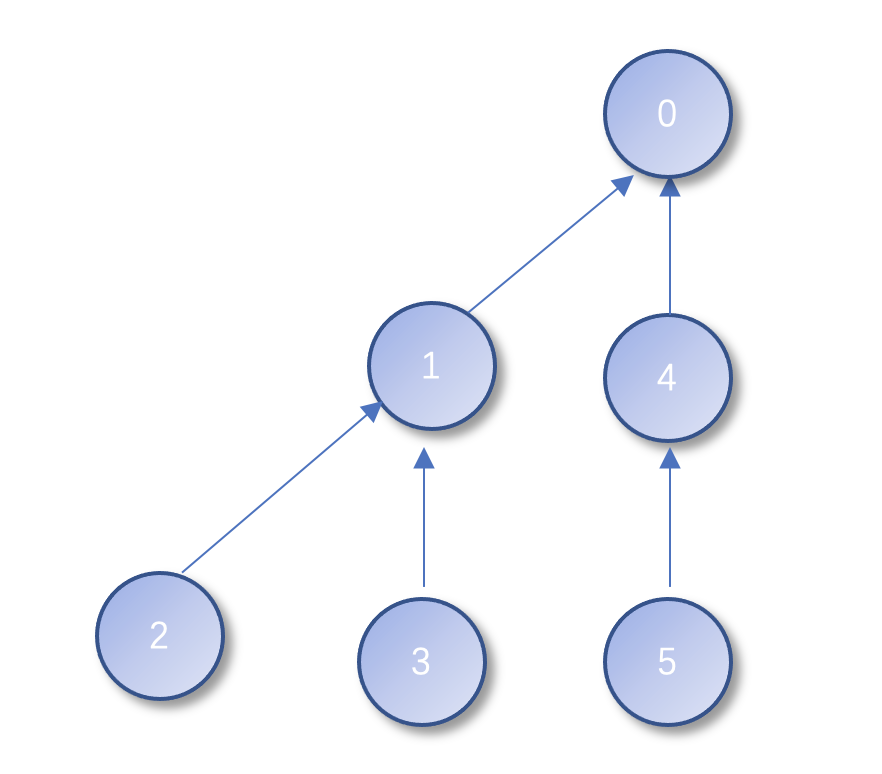
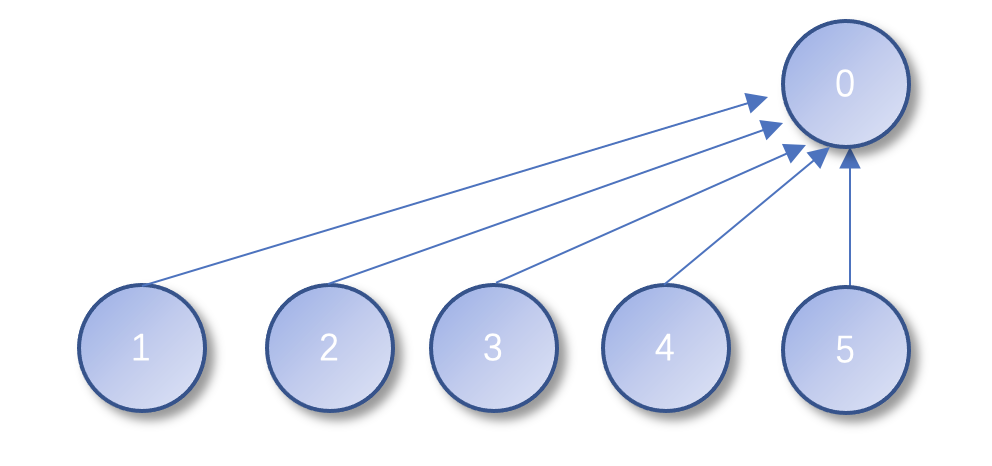
减少树的层数,这个过程就叫做路径压缩。
这里我们可以使用递归来执行,终止条件是查询到根节点,非终止条件的传递操作就是将parents里该节点的设定成父节点的父节点。
路径压缩在我们处理加权并查集的时候会使用到,这里我们再使用按秩优化,顺便加上权,代码如下:
基础数据
- // 树
- int[] parents;
- // 权
- double[] weights;
- // 秩
- int[] size;
初始化方法
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.parents = new int[n];
this.weights = new double[n];
this.size = new int[];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parents[i] = i;
weights[i] = 1.0d;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
find函数
public int find(int x) {
assert (x<0 || x >= parents.length);
if (x != parents[x]) {
int origin = parents[x];
parents[x] = find(parents[x]);
weights[x] *= weights[origin];
}
return parents[x];
}
union函数
public void union(int x, int y, double value) {
int xRoot = findRoot(x);
int yRoot = findRoot(y);
if (xRoot != yRoot) {
if (size[xRoot] > size[yRoot]) {
parents[yRoot] = xRoot;
size[xRoot] += size[yRoot];
// weights[xRoot] = 1
// weights[yRoot = 1
// weights[x] = m
// weights[y] = n
// value = m / n
// 合并以后
// weights[xRoot] = 1
// weights[x] = m
// weights[y] = m / value
// weights[yRoot] = m / (value*n)
weights[yRoot] = weights[x] / (weights[y] * value);
} else {
parents[xRoot] = yRoot;
size[yRoot] += size[xRoot];
// weights[xRoot] = 1
// weights[yRoot = 1
// weights[x] = m
// weights[y] = n
// value = x / y
// 合并以后
// weights[yRoot] = 1
// weights[y] = n
// weights[x] = n * value
// weights[xRoot] = (value*n) / m
weights[xRoot] = weights[y] * value / weights[x];
}
}
}
查找权重方法
public double isConnected(int x, int y) {
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if (xRoot == yRoot) {
return weights[x] / weights[y];
} else {
return -1.0d;
}
}
要特别注意的一点是,因为压缩路径以后的并查集只有两层,根节点的权为1,所以执行find函数的时候,即便每次都要向上查询根节点,并且乘以根节点的权,得到的还是自己本该有的权。
Tips:并查集的操作时间复杂度
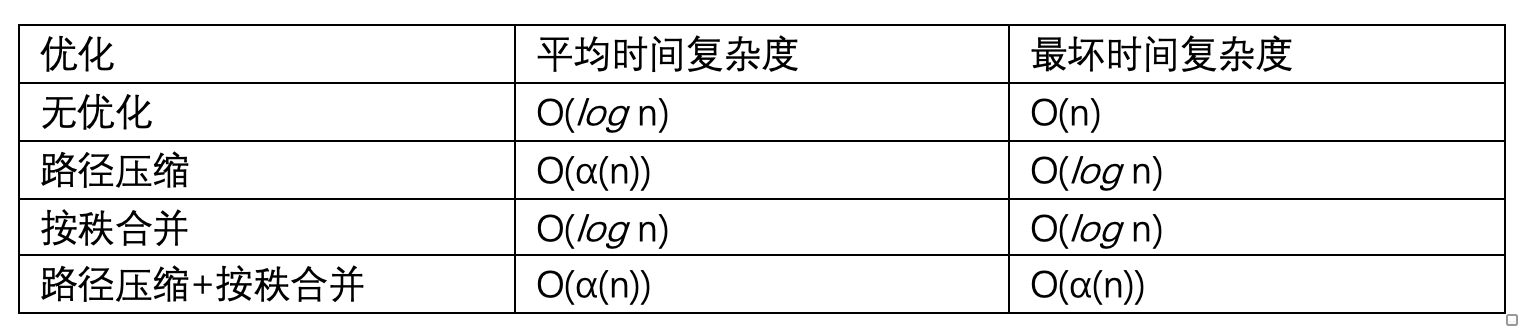
这里的α 表示阿克曼函数的反函数,在宇宙可观测的 n 内(例如宇宙中包含的粒子总数),α(n) 不会超过 5。